Apache vs Nginx with Wordpress
Introduction
Previously we’ve shown how to use apache server for hosting Wordpress sites and use the right MPM to get a better performance, now we will explore another popular web server called Nginx and compare its performance with apache and event MPM.
Nginx is a popular web server software written in C, it can be used as a reverse proxy, caching server and load balancer, it offers very high performance without changing the configuration, Nginx does not have any modules to execute PHP scripts in its own process, it relies on other servers to execute them and return the results.
To follow along make sure you have read the previous tutorial and you have the results ready to compare them with the results you will get here.
What will we do?
In this tutorial we will:
- Install Nginx server and use it to serve Wordpress site.
- Run locust performance tests on the server and compare them with previous results.
Nginx installation
Login to the wordpress droplet created previously and execute these commands to install Nginx
systemctl stop apache2
apt install nginx -y
First we stopped apache2 server so when we install Nginx it starts immediately, because Nginx and Apache use port 80 for listening to HTTP connections and we cannot start them both at the same time.
If you try to access your wordpress site now you will get “403 Forbidden” as shown bellow
This is because Nginx needs additional configuration to execute PHP scripts, we will explore this in the next section.
Configure Nginx to execute PHP
By default Nginx will just return the contents of PHP files when we request them, but we need to execute these files and return the results.
In order to do this we will change the default Nginx site located in
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default and add these lines.
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
Here we tell nginx to use the configuration for all files that end with .php
extension, first we include the configuration options located in snippets/fastcgi-php.conf then we tell nginx where to find the PHP-FPM socket using fastcgi_pass option.
After we make these changes we restart Nginx using this command for changes to take effect.
systemctl restart nginx
If we try to access Wordpress site again we will see that we still have the
same error “403 Forbidden”, now nginx is configured to execute PHP scripts
if we try to call them directly in the URL, try to create a simple PHP script
inside the Wordpress directory called info.php with this content and request
it from the browser using this URL http://<wordpress_ip>/wordpress/info.php
and it will work as shown bellow
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
In the next section we will explore the source of this error and configure Nginx properly to serve Wordpress site.
Configure Nginx to serve Wordpress site
When we used Apache, it was able to serve Wordpress sites without any configuration
thanks to the .htaccess file that comes with Wordpress code, this file includes
directives to properly rewrite URLs to include the PHP script name in the URL
so the server can properly execute the file, however Nginx does not use or read
.htaccess files for performance reasons as this file is read every time a new
request is received and this will slow down the server.
So the configuration to rewrite the URLs in Nginx must be added to Nginx site manually and this configuration is read once when Nginx starts and never changed untill nginx is restarted, so the configuration is not read from the disk for every new request and this will improve performance and reduce disk reads when serving requests.
Open your default nginx site configuration file and add these lines of code.
location /wordpress {
rewrite ^(/[^/]+)?(/wp-.*) /wordpress/$2 break;
rewrite ^/wordpress/(.*)$ /wordpress/index.php?q=$1 last;
}
This block is applied only when we open a Wordpress URL (it starts
with /wordpress) remember we put wordpress code in a sub-directory, we
have two rewrite rules here, the first one for all URLs that end with
wp- prefix such as /wordpress/wp-admin and /wordpress/wp-login and the second one
is for URLs that start with wordpress prefix, they are rewrote
to include index.php file.
Now restart Nginx and try to open wordpress site again.
systemctl restart nginx
if you get any errors, here is the complete Nginx configuration file,
make sure it matches your file and do not forget ; at the end of lines.
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
root /var/www/html;
index index.html index.htm index.nginx-debian.html;
server_name _;
location /wordpress {
rewrite ^(/[^/]+)?(/wp-.*) /wordpress/$2 break;
rewrite ^/wordpress/(.*)$ /wordpress/index.php?q=$1 last;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
}
}
Load test Nginx
Now after nginx is configured and ready to serve our Wordpress site, we need to run load tests against it as we did with Apache, to do this login to the locust droplet and execute this command
locust --no-web -c 500 -r 50 -t2m --only-summary --csv=500.50
The following image shows the results
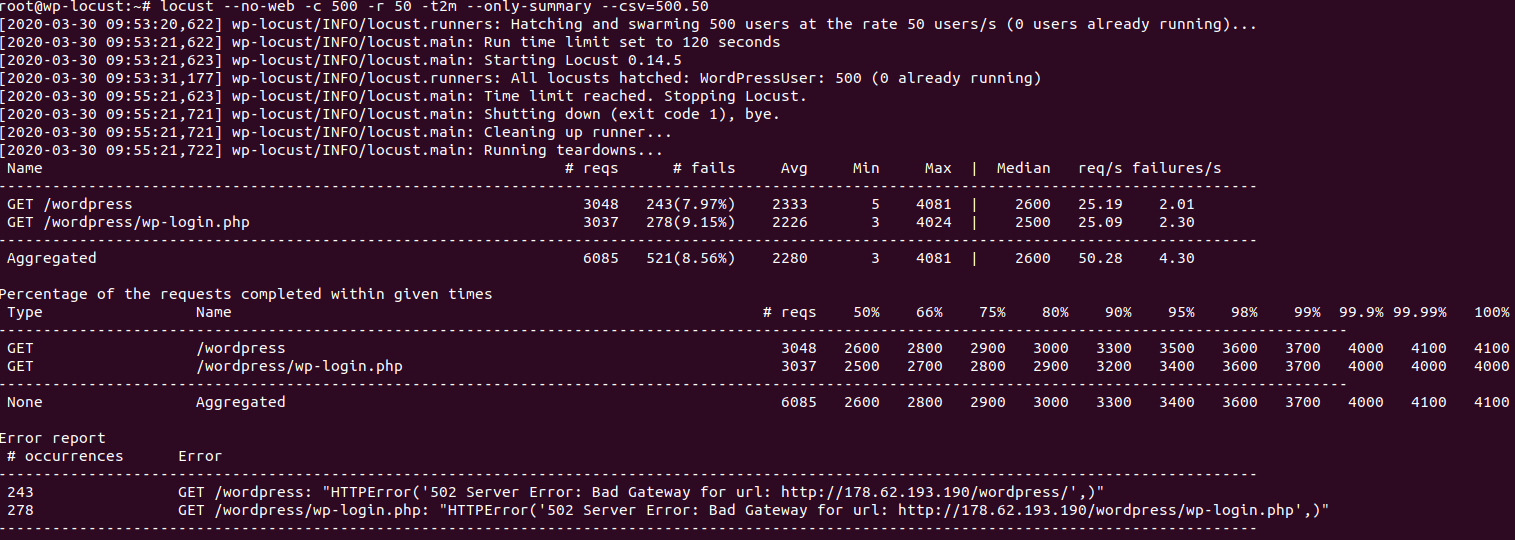
From the image we can see the average response time is 2.2 seconds, this is very close to the one we got from apache event MPM, however for the errors we can see a lot of them 521 errors and the requests per second is 50.28 very close to the value we got with apache event MPM.
Conclusion
In this tutorial we learned how to use nginx to serve Wordpress sites, we also made load tests on Nginx and compared them with apache tests.
From the previous results in this tutorial and the previous one we can find these conclusions:
- Apache prefork and worker MPMs are not suitable at all for Wordpress sites, DO NOT USE THEM.
- Apache event MPM offers a great performance for Wordpress sites.
- Nginx out of the box can offer very good performance for Wordpress sites, however with high load we got a bigger number of errors than with apache.
You could try for your self and test apache vs nginx using different number of users and different hatch rates (number of users added per second) and share results in the comments bellow.
In future tutorials we will focus on using multiple droplets for our Wordpress sites to provide better performance and highly available infrastructure.
I hope you find the content useful for any comments or questions you can contact me on my email address mohsen47@hotmail.co.uk
Stay tuned for more articles. :) :)